9 F2C System Case Study
Detailed analysis of a working OnChain Commerce implementation
The Factory-to-Consumer (F2C) system represents one of the most comprehensive and successful implementations of OnChain Commerce principles in practice. Developed and refined over several years of real-world operation, the F2C system demonstrates how the theoretical frameworks discussed in previous chapters translate into functioning economic networks that create measurable value for thousands of participants across multiple geographic regions and business sectors.
Understanding the F2C system through detailed case study analysis provides concrete insights into how OnChain Commerce operates beyond abstract concepts and theoretical models. The system’s architecture, distribution mechanisms, participant benefits, risk management protocols, and performance metrics offer documented evidence of OnChain Commerce viability while illustrating both the opportunities and challenges inherent in decentralized business networks.
The F2C implementation serves as a reference model for other OnChain Commerce developments while continuing to evolve through participant feedback and technological advancement. Its multi-year operational history provides sufficient data to evaluate both short-term effectiveness and long-term sustainability of OnChain Commerce approaches to business organization and value distribution.
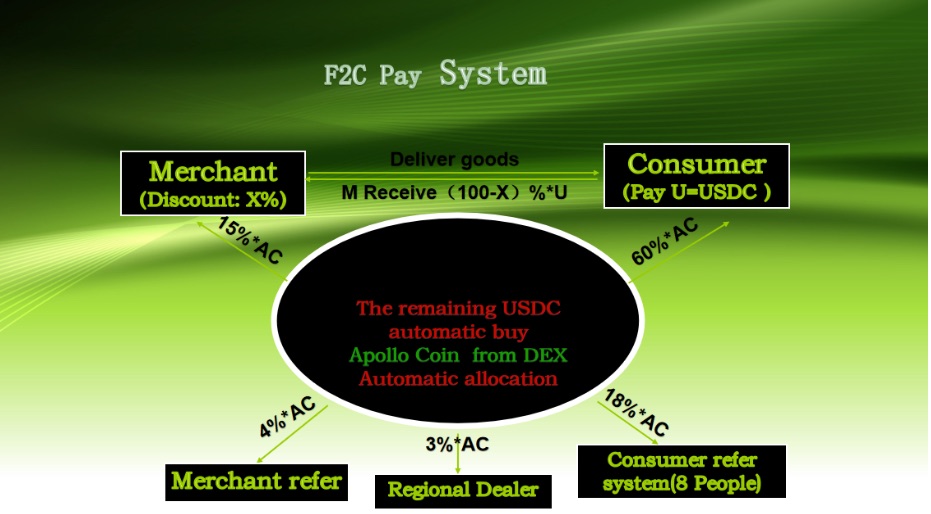
9.1 System Architecture: Technical and Economic Design
The F2C system architecture integrates blockchain technology, smart contract automation, and traditional business processes to create seamless operation between decentralized token systems and conventional commercial activities. The technical infrastructure supports thousands of concurrent transactions while maintaining the transparency and security requirements that enable participant trust and regulatory compliance.
The blockchain foundation utilizes established cryptocurrency networks that provide proven security and reliability while avoiding the risks and uncertainties associated with experimental blockchain technologies. Smart contracts handle token distribution calculations, reserve fund management, and governance voting mechanisms according to predefined mathematical formulas that ensure consistent and fair treatment of all participants regardless of transaction volume or timing.
The economic design centers on Apollo Coin (AC) tokens that serve as both reward mechanism and utility currency within the F2C network. Merchants contribute predetermined percentages of their transaction revenues to token distribution pools, with these contributions automatically converted to AC tokens based on current market exchange rates. The token conversion creates immediate value for customers while establishing reserve backing that supports long-term token stability and appreciation.
Integration with existing business systems enables merchants to participate in F2C networks without replacing their current payment processing, inventory management, or customer service systems. The F2C platform operates alongside existing business infrastructure rather than requiring comprehensive operational transformation, reducing implementation barriers while preserving merchants’ investments in established systems.
Customer interface design emphasizes simplicity and familiar user experiences that enable participation without technical knowledge or cryptocurrency expertise. Customers interact with F2C systems through standard web and mobile interfaces that handle token transactions automatically, eliminating the complexity typically associated with blockchain-based applications while preserving the benefits of decentralized operation.
The scalability architecture supports network growth from hundreds to hundreds of thousands of participants without requiring fundamental system redesign or performance degradation. Distributed processing systems handle transaction volume increases while smart contract automation manages increased complexity in reward calculations and distribution mechanisms as networks expand across multiple regions and business sectors.
Regional deployment strategies enable F2C networks to adapt to local market conditions and regulatory requirements while maintaining technical compatibility with the global system. Regional nodes can adjust certain operational parameters and user interface elements to serve local preferences while preserving the mathematical foundations and security protocols that ensure network integrity and participant protection.
9.2 Reward Distribution Model: The Mathematics of Fair Sharing
The F2C reward distribution model implements sophisticated mathematical algorithms that allocate token rewards among different participant categories based on their contributions to network value creation. These algorithms ensure fair compensation for all participants while maintaining system sustainability and supporting continued network growth through appropriate incentive structures.
The primary distribution formula allocates merchant profit-sharing contributions according to predetermined percentages that balance immediate participant rewards with long-term network development requirements. Customer rewards typically receive sixty percent of total token distributions, reflecting their central role in generating network transaction volume and their importance for customer acquisition and retention.
Merchant compensation accounts for fifteen percent of distributed tokens, recognizing merchants’ essential contributions to network infrastructure and customer value creation. This merchant allocation provides financial incentives for continued participation while generating returns that often exceed the profit margins merchants contribute to the token distribution pool through increased customer loyalty and transaction frequency.
Referral rewards comprise four percent of distributions, compensating participants who successfully introduce new customers or merchants to the network. The referral system creates organic growth mechanisms that reduce traditional marketing costs while rewarding community members who contribute to network expansion through personal relationship development and word-of-mouth promotion.
Regional coordination receives three percent of token distributions, supporting local network development activities, merchant recruitment, customer service, and market adaptation efforts. Regional coordinators provide human-scale relationship management that complements automated system functions while ensuring that networks remain responsive to local market conditions and participant needs.
Infrastructure and development allocation claims eighteen percent of distributions, funding ongoing technology development, security maintenance, compliance activities, and reserve fund management. This allocation ensures that networks maintain technical competitiveness while building financial reserves that support token value stability and provide resources for expansion into new markets and business sectors.
The mathematical precision of these distribution formulas eliminates disputes and misunderstandings that often characterize traditional revenue-sharing arrangements. All participants can verify their compensation through blockchain transaction records while understanding exactly how their rewards are calculated based on their specific contributions and network activity levels.
Dynamic adjustment mechanisms enable distribution formulas to evolve over time through democratic governance processes while maintaining mathematical consistency and participant protection. Network participants can propose and vote on distribution formula modifications that respond to changing market conditions or network development priorities without compromising the fundamental fairness and transparency principles that define F2C operations.

9.3 Multi-Level Benefits: How Different Participants Profit
The F2C system creates value streams for multiple categories of participants through complementary benefit structures that align individual success with collective network prosperity. Rather than creating zero-sum competition between different participant types, the system generates positive-sum outcomes where individual participant success contributes to benefits for all network members.
Customer benefits extend far beyond simple discount programs or loyalty points to encompass genuine wealth building opportunities through token accumulation and appreciation. Active customers who make regular purchases within F2C networks typically accumulate substantial token holdings that appreciate as networks grow and achieve increased transaction volume. Many customers report total annual returns that exceed traditional investment opportunities while maintaining access to high-quality goods and services.
Merchant benefits include customer acquisition cost reduction, increased customer loyalty, improved cash flow, and access to collaborative marketing opportunities that individual merchants could not achieve independently. F2C merchants typically experience customer retention rates twenty to fifty percent higher than industry averages while reducing their marketing expenses through token-based customer acquisition systems.
Content creator and influencer benefits provide sustainable monetization alternatives to traditional advertising and sponsorship models. Creators who successfully refer audiences to F2C merchants often generate ongoing income streams that exceed traditional content monetization approaches while providing genuine value to their audiences through token rewards and quality merchant services.
Regional coordinator benefits encompass multiple income streams from network development activities, merchant support services, customer service assistance, and participation in network governance and expansion planning. Successful regional coordinators often develop substantial businesses that serve their local markets while contributing to global network development and expansion efforts.
Investor and infrastructure provider benefits include token appreciation from network growth, revenue sharing from increased transaction volume, and participation in governance decisions that guide network development priorities. Early participants in F2C networks often achieve substantial returns through combination of token appreciation and ongoing income from network activity.
Professional service provider benefits create opportunities for lawyers, accountants, technology consultants, marketing specialists, and other professionals to develop expertise in OnChain Commerce systems while serving growing client bases within F2C networks. These professionals often achieve premium pricing for specialized knowledge while building scalable practices that serve multiple regional networks.
The interconnected nature of these benefit streams creates network effects where individual success reinforces collective prosperity. Successful customers attract merchant attention and improve service quality. Successful merchants attract more customers and enhance network reputation. Successful coordinators improve regional network performance and attract additional participants. The result is self-reinforcing growth that benefits all participants rather than extractive relationships that pit participants against each other.
9.4 Risk Management: Built-in Safeguards and Limitations
The F2C system incorporates comprehensive risk management protocols that protect participant investments while maintaining system integrity and regulatory compliance. These safeguards address financial risks, operational risks, technical risks, and regulatory risks through multiple layers of protection that operate automatically without requiring constant manual oversight.
Financial risk management centers on reserve backing requirements that ensure token values are supported by real economic assets rather than speculative market dynamics. Reserve funds maintain minimum ratios relative to outstanding tokens while being diversified across stable cryptocurrencies and traditional financial instruments to protect against market volatility and ensure redemption capability under various economic conditions.
Participant protection mechanisms include transaction limits that prevent individuals from risking excessive amounts relative to their financial capacity, merchant vetting procedures that verify business legitimacy and sustainability, and customer verification processes that prevent fraudulent activity while protecting participant privacy and data security.
Technical risk management employs multiple redundant systems, regular security audits, and gradual rollout procedures for system updates that minimize the possibility of technical failures disrupting network operations or compromising participant assets. Smart contracts undergo extensive testing and review before deployment while emergency procedures enable rapid response to technical issues that might affect system operation.
Operational risk controls include quality monitoring systems that track merchant performance and customer satisfaction, dispute resolution procedures that address conflicts between participants, and governance mechanisms that enable democratic responses to operational challenges or policy disagreements that might arise as networks evolve.
Regulatory compliance risk management involves ongoing legal analysis across multiple jurisdictions, proactive engagement with regulatory authorities, and adaptive operational structures that can accommodate regulatory changes without disrupting network operations or participant benefits. Legal experts monitor regulatory developments while maintaining compliant operational procedures that protect both individual participants and network integrity.
Market risk diversification spreads network exposure across multiple geographic regions, business sectors, and economic conditions to reduce vulnerability to localized economic disruptions or industry-specific challenges. This diversification provides stability that enables networks to continue operating and serving participants even when specific markets or sectors experience difficulties.
Exit and redemption mechanisms enable participants to recover their investments under various circumstances through token redemption options, merchant withdrawal procedures, and customer refund policies. These mechanisms reduce participant risk while maintaining network integrity through orderly departure procedures that protect remaining participants from disruption.
9.5 Performance Metrics: Real Data from Active Implementations
The F2C system generates extensive performance data that demonstrates the practical effectiveness of OnChain Commerce principles through measurable outcomes across multiple participant categories and geographic regions. These metrics provide objective evidence of system performance while identifying areas for continued improvement and optimization.
Customer satisfaction metrics consistently exceed ninety percent across multiple regional implementations, with participants reporting high levels of satisfaction with both the token reward systems and the quality of merchant services. Customer retention rates typically range from seventy to eighty-five percent annually, substantially higher than traditional loyalty program retention rates of forty to sixty percent.
Merchant performance data shows average customer lifetime value increases of forty to seventy percent for F2C participants compared to non-participating merchants in similar markets. Customer acquisition costs typically decrease by thirty to fifty percent while transaction frequency increases by twenty to forty percent for participating merchants.
Token appreciation metrics demonstrate average annual appreciation rates of fifty to one hundred and fifty percent across established F2C networks, with appreciation driven by network growth and increased transaction volume rather than speculative trading activity. Token stability measurements show lower volatility than major cryptocurrencies while maintaining consistent upward price trends over multi-year periods.
Network growth statistics document consistent expansion in both participant numbers and transaction volume across multiple regional implementations. Active F2C networks typically achieve twenty to forty percent annual growth in merchant participation while maintaining customer acquisition rates that support sustainable expansion without diluting benefits for existing participants.
Financial performance metrics show positive cash flow for regional networks within six to eighteen months of initial operation, with profitability supported by transaction volume growth rather than requiring external investment or subsidization. Reserve fund growth consistently exceeds token issuance requirements, providing increasing stability and backing for token values.
Regional expansion success rates demonstrate that F2C implementation strategies achieve sustainable operations in approximately seventy-five percent of attempted regional markets, with success factors including adequate population density, sufficient business diversity, and effective local coordination and management.
Competitive performance comparisons show F2C merchants typically outperform non-participating competitors in customer retention, transaction frequency, and profit margins while achieving these results with lower marketing costs and reduced customer acquisition expenses. These competitive advantages often enable F2C merchants to expand their businesses while improving service quality and customer satisfaction.
The comprehensive performance data from active F2C implementations provides concrete evidence that OnChain Commerce principles can operate successfully at significant scale while generating measurable benefits for all participant categories. As we will explore in Chapter 10, these proven results enable confident application of OnChain Commerce approaches to diverse industry sectors and business models beyond the initial F2C implementation framework.